My sole intention for writing this piece is to prevent investors from losing more money in the stock market.
Allow me to tell you briefly my back ground so that you can accept my advice to ask you to cash out from the stock market.
Dato Yap Lim Sen, my collegemate and I were the original founders of Mudajaya, Gamuda, IJM, IGB, Rubberex, MBM Resources, major controlling shareholder of Perodua Cars.
I have been investing in the stock market for more than 50 years. This is the first time I have practically sold all my stocks holdings and cashed out.
When you buy a stock, you hope to gain from share price increase and also dividend yield. In Malaysia all listed companies give out very small dividend. On record, Public Bank gives out the best dividend yield of about 5% per year. So, unless the stock price goes up, investors cannot make money.
What pushes the share up?
Among all the stock selection criteria such as account balance sheet, cash flow, NTA, no debt or cash rich etc, profit growth prospect is the most powerful catalyst to push up share price. Never buy any stock that has no profit growth prospect.
Why investors must believe in price chart?
Price chart cannot lie because it is a record of the daily trading. Down trend means there are more sellers than buyers in most days. Never buy a down trending stock.
A stock price can only go up if the company has reported increased profit. But if it reports reduced profit, its share price would drop because there would be more smart sellers than stupid buyers.
In the last 6 months, almost all the listed share prices have been dropping as shown on the KLCI Chart below. Why?
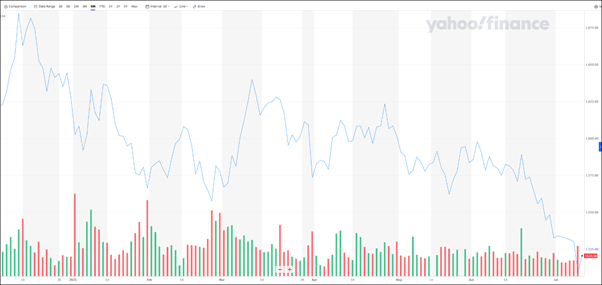
There are 2 main reasons for the listed companies’ share prices to drop.
1 Covid 19 pandemic
Covid 19 pandemic frequent lockdown restricts people’s movement and all listed companies’ business operation. Workers cannot go to work and business activities are reduced. As a result, almost all listed companies cannot report increased profit in the next few quarters until Covid 19 pandemic is fully under control. Many medical experts predicted that the pandemic will not be under control for at least 1 or more years. That simply means our stock market will be depressed for at least 1 or more years. The above KLCI chart shows that it has been dropping for the last 6 months and it will continue to drop for another 1 or more years.
2 Political Uncertainty
Investors do not like political uncertainty. In the last general election about 2 years ago, Pakatan Harapan won the right to form the Government and Dr Mahathir became the Prime Minister. Within a couple of months, he resigned suddenly and Muhyiddin became the PM by the back door. Currently he is seriously terminally ill with cancer in KL Hospital. Apparently, he has pancreatic cancer.
Who will be the next PM?
As you know, Politicians make rules and regulations which often affect business operation and their balance sheets which is creating more difficulties in making investment decisions.
That is why many investors especially foreign institutional investors are constant net sellers and some of them have already left the stock market.
Yesterday I posted my article namely “A safe strategy during the pandemic” in which I said the Covid 19 pandemic lockdown is affecting everybody’s movement. Workers cannot to go to work and all business operation will naturally slow down. Almost all the listed companies will not be able to report increased profit in the next few quarters until the Covid 19 pandemic is fully under control which will take at least 1 or more years.
For example:
All the steel products manufacturers have reported increased profit in their latest quarter due to the steel price increase. Currently, due to Covid 19 pandemic lockdown, workers cannot go to work to make steel products and construction workers also cannot go to work. Contractors will not require to buy steel products. As a result, all the steel products makers will report reduced profit in the next few quarters. Many smart investors already could foresee this situation. That is why Leon Fuat, the most profitable steel company price chart is showing down trend as you can see below.
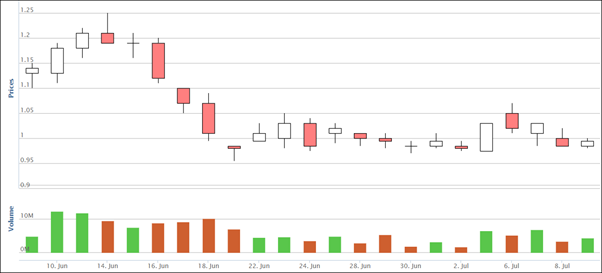
Leon Fuat’s last traded price is 99 sen and its latest EPS for quarter ending March 2021 was 11.65 sen. Even if I assume its EPS for the next 3 quarters is the same as 11.65 sen, its annual EPS will be 46.6 sen. Leon Fuat is selling at PE 2.
Other Industries also suffer the same fate
In fact, almost all other industries also suffer the same fate as steel companies. For example, Supermax and Top Glove have to close down a few times because the government authorities found Covid 19 cases in their factories.
Supermax price chart below:
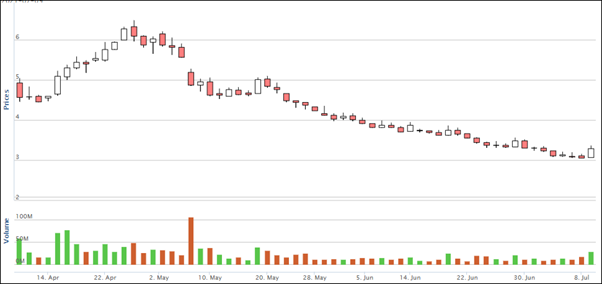
Investors must always remember price chart is the more important investment consideration than financial analysis. Down trend price chart means there are more smart sellers than stupid buyers.
Statistics shows that in the stock market, there are about 70 % of investors lose money, 10% of investors break even and only 20% of investors are real winners. But under the current condition all investors including myself are losing money.
All investors must examine their track record to their performance. Even if they have been winners, they should sell all their holdings as soon as possible before they lose more money and get out of the stock market completely.
My mistake
I must admit my mistake in recommending Leon Fuat recently because I did not foresee earlier how Covid 19 lockdown and our political uncertainty can cause serious damage to the stock prices. That is why I sold practically all my stock holdings and cashed out of the stock market.
A
best strategy during the pandemic for all investors is to cash out
because all listed companies will not be able to report increased profit
in the next quarters..
More articles on Koon Yew Yin's Blog >>
- A safe strategy during pandemic - Koon Yew Yin - Jul 10, 2021
- What is the fastest way for Malaysia to stop Covid-19? Koon Yew Yin - Jul 10, 2021
- What do women really want? Koon Yew Yin - Jul 07, 2021
- Glove supply exceeds demand - Koon Yew Yin - Jul 06, 2021
- Leon Fuat is best steel stock to buy? Koon Yew Yin - Jul 05, 2021
- I had heart bypass surgery in 1983 and how pineapple prolongs my life - Koon Yew Yin - Jul
Related posts:













