A property, no matter how great-looking it is, is only as good as its management and maintenance. It will look clean and polished when it is new but the good news is, it can still look as good even as it ages.
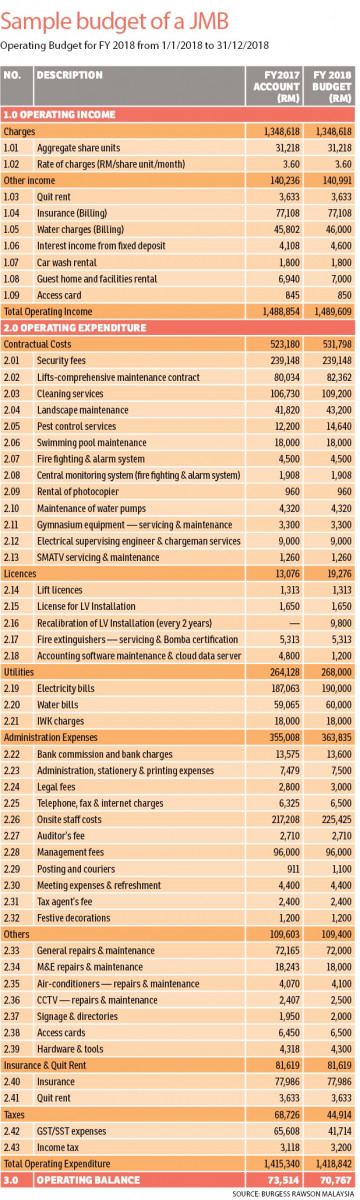
According to the Strata Management Act 2013 (SMA 2013) which came into effect in June 2015, a strata owner or occupier needs to pay a monthly maintenance fee or service charge to the Joint Management Body (JMB) or Management Corporation (MC) which will be used to manage and maintain the common property of the development.
Other than the maintenance fee, strata owners are also required to contribute to the sinking fund which is normally at the rate of 10% of the total amount of charges.
“A sinking fund is a reserve fund collected from the strata owner for future expenditure which is typically less predictable and cost a lot more than the usual maintenance fee. The sinking fund is usually used for large scale repairs such as a painting job or refurbishment of the interiors of common facilities,” says Chur Associates managing director Chris Tan.
However, some owners may feel that the maintenance fee is too much. But how much is too much? How is the fee amount calculated or set? Is there a formula or a guideline?
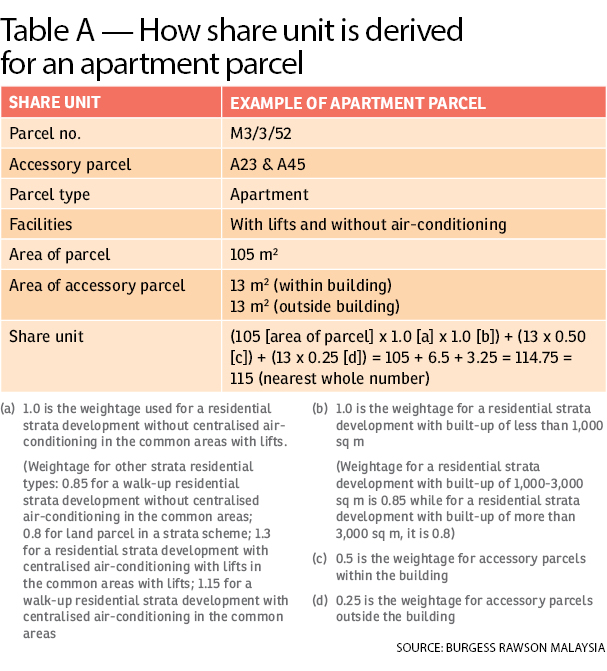
Formula to derive the share units
Under the SMA 2013 and Strata Titles Act 1985 (STA), a residential or commercial unit is technically known as a parcel and each parcel has a share value that is expressed in whole numbers under the STA.
“Upon the approval of computation and allocation of share units prepared by the licensed land surveyor, the director of Land and Mines will issue the Certificate of Share Unit. To derive the share units in a strata scheme, there is a standard formula under the Fourth Schedule of the Strata Titles Rules 2015,” explains Burgess Rawson Malaysia managing director Wong Kok Soo.
The standard formula for maintenance fee:

What does the maintenance fee cover?
The MC chairman of Sri Penaga, one of Bangsar’s oldest condominiums, Khaw Chay Tee shares with EdgeProp.my that one of the biggest components in the operations expenditure of a residential condominium is security, followed by the property management staffing and cleaning.
“Normally these components make up 50% of your service charge. So at the end of the day, it really boils down to how well-managed that property is. If you are able to manage the property well, then you can keep the cost reasonable. There are some condominiums where the MC likes to carry out projects which incur costs, but that is a separate matter. As each condominium differs in its number of facilities and the density of the development, it is not so easy to compare and ask why this condominium in Bangsar is different from that condominium in Bangsar,” says Khaw.
Knight Frank senior executive director Kuruvilla Abraham concurs that the service charge will vary depending on the service level the JMB or MC requires.
“One can find cheaper options for the various services required which no doubt will result in lower service charges. However, don’t expect good service levels. The right thing to do is to get value-for-money services that commensurate with the expected service levels,” he says.
It also depends on the design of the development, he adds.
“The development with a reasonable number of facilities and a greater number of units will generally pay a lower proportion of service charge compared to one with similar facilities but with lower density.”
Furthermore, developments with more facilities such as fountains, gardens or swimming pools would naturally command a higher fee as more maintenance is needed.
When it comes to maintenance, the level of quality is subjective, reminds Chur Associates’ Tan. Hence, questions often arise on whether what they are paying is actually put to good use.

“What is the definition of “clean” to you? For some, clean means I don’t see any rubbish. For others, it means it has to be squeaky clean and sparkling. We cannot even come up with an industrial standard for door size and window size, how do we even budget the cleaning cost then? If I were the cleaning company, how would I charge you if your windows are bigger than others? Do I charge more? Or can I say the unit price is RM2 per window per cleaning [regardless of size]?” Tan questions.
He adds that the priorities of residents in different projects mean the maintenance fee charged for each development would be different.
“Some residents place a lot of emphasis on security, so they would rather [the JMB or MC] spend more money hiring guards from a prestigious company while there may be some who think that [the JMB or MC] should spend the money to clean the swimming pool daily because they use it often,” he explains.

The problem with a low maintenance fee
The Malaysian Institute of Property and Facility Managers (MIPFM) president Sarkunan Subramaniam tells EdgeProp.my that problems often arise when the property developers set a lower-than-normal maintenance fee in the initial period to induce sales.
“During the first two years, the equipment is still under the defects and liability period, so if say, the swimming pool has an issue, you can just call the technician to come over for free. However, when the JMB or MC takes over when the warranty period has passed, cost will start to be incurred,” says Sarkunan.
Under the STA 2013, developers are not supposed to pass on any deficits or liabilities to the JMB and MC.
Chur Associate’s Tan says problems can also crop up later when a developer designs a very over-the-top facility or development but prices the property at a low selling price, hence attracting the wrong user/buyer profile to the project.

“If I ask you what you want in your development, you will surely say you want everything. But nobody tells you that in order to have everything, moving forward, the monthly contribution will be higher. When the entry point is low, everybody wants to buy but nobody thinks about the maintenance fee in future.
“On many occasions, it is not about who gives the best facility but who is paying for it. Are you going to use it? How often do you go to your condo’s gym or would you rather go to a gym outside? Why? Maybe because you have your own personal trainer or you don’t want to be seen by your neighbour. So are we overdesigning and overproviding?” Tan questions.
In accordance with the Strata Management Act 2013 (Act 757) (SMA), developers shall hand over the maintenance and management of the strata development (common property) to the JMB not later than 12 months of vacant possession or the MC, should the strata titles be issued and transferred to the purchasers, whichever is earlier.
The items developers are required to hand over include the list of assets, fixtures and fittings, as-built plans, operation manuals as well as the audited accounts of the service charges, deposits and sinking fund as prescribed under the SMA via Form 4 (for JMB) and Form 13 (for MC).
The JMB and MC can then decide by votes or by appointing a registered property management company to suggest an amount for the maintenance fee.
“The owner has the right to request to see the accounts during the Annual General Meeting related to expenditure and raise the matter during the meeting,” says Knight Frank’s Kuruvilla.
However, he points out that he has yet to come across a developer that has charged the parcel owners more than what they are supposed to pay. In fact, the chances are higher that due to non-payment, the management account is likely to be in deficit resulting in there being insufficient funds to carry out proper maintenance and management of the development.
The problem with strata living is, everybody wants to have a well-maintained place to live but not everyone is prepared to pay for it.
“This is why the government passed the Strata Management Act 2013 (and Acts before this) so that after one year post development, it will give the parcel purchasers/proprietors the opportunity to manage the property and thereby giving them an understanding by getting first-hand knowledge in what it takes to maintain and manage a development well. Until one is directly involved, one will not be able to appreciate why service charges have to be paid on time to ensure there is sufficient funds to pay for the maintenance and management of the development.”
This story first appeared in the EdgeProp.my pullout on Nov 30, 2018. You can access back issues here..
Related posts:
Separate role for property managers
High-rise living in below par, need professionalism in managing the property
STRATA Property insights - Serious on strata
Invest in the future
Young adults in developed countries rent, we buy houses for good
Instead of blowing their cash on pricey gadgets, young Malaysians are saving up for their first home.