PETALING JAYA: Although no new mpox cases have been reported in Malaysia so far this year, the Health Ministry says it is ramping up surveillance and advocacy activities after the World Health Organisation (WHO) issued its highest alert.
The ministry said Malaysian authorities are stepping up surveillance at international entry points and all travellers from countries that have reported mpox cases are required to monitor their health status, including symptoms for 21 days after their arrival in Malaysia.
It also advised people with a history of risky activities or who have symptoms such as rashes and blisters to seek treatment at the nearest health facility immediately and avoid contact with other people to prevent the spread of the virus.
Healthcare personnel at public and private facilities are also required to notify suspected and confirmed cases to their nearest district health office to ensure that prevention and control measures can be implemented.
The ministry also assured the public that there are enough labs for testing and diagnostics.
There are 10 labs, including two private labs, with the capability to conduct PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests to confirm any diagnosis.
The ministry is also increasing awareness activities by distributing materials to high-risk groups and locations, such as spas and saunas.
It said premises offering services that involve skin-to-skin contact with customers such as the aforementioned must always ensure that hygiene is maintained and their employees as well as customers are not experiencing symptoms such as blisters or rashes.
“If an employee or customer experiences symptoms, they should immediately seek medical attention,” the ministry said in a statement yesterday.
It added that it will continue to work with other government agencies and non-government agencies including public hospitals and private hospitals to monitor, detect and treat mpox cases.
It will also continue to monitor the situation within and outside the country.
WHO had declared mpox, previously known as monkeypox, a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) for the second time on Aug 14.
The first PHEIC was declared on July 23, 2022, and ended on May 11, 2023.
“The second declaration was made based on the advice of the IHR (International Health Regulations) Emergency Committee given the spread of the new mpox strain known as clade 1b, which is spreading fast in the Democratic Republic of Congo and neighbouring African countries,” it said.
“The increase in cases in Congo is quite significant with 15,600 cases and 537 deaths reported in 2024, which is higher than the year prior.
“Apart from that, four countries in East Africa, namely Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda and Uganda, reported mpox cases for the first time,” it added.
Malaysia has recorded nine mpox cases to date since the first case was detected on July 26, 2023, including a case recorded in November that year.
The Health Ministry said all the cases reported had a history of high-risk activities and had recovered with no deaths reported.
Commenting on the latest development, Prof Dr Sharifa Ezat Wan Puteh, a health economics and public health specialist with Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia’s Faculty of Medicine, said those who had sexual encounters with partners from countries where there are mpox cases, including places where the disease is endemic, should be monitored.
“It can also spread from infected pregnant women to their unborn children.
“Those travelling out to infected countries, especially the United States and African countries, need to be mindful of the risk of contact and infection during sexual activities,” she said.
A total of 99,176 mpox cases, including 208 deaths, were reported worldwide from Jan 1, 2022 to June 30, 2024.- THE STAR/ASIA NEWS NETWORK
China implements measures to prevent mpox at ports
People coming from countries and regions affected by mpox outbreak, who have been exposed to mpox or have symptoms such as fever, headache, back pain, muscle pain, swollen lymph nodes and rashes, should declare their conditions to customs upon entry. Customs officials will take medical measures and conduct sampling tests according to prescribed procedures, the GAC said.
Transport vehicles, containers, goods, and items from countries or regions affected by the outbreak and potentially contaminated should undergo sanitary treatment according to prescribed procedures, the GAC noted.
The measures took effect immediately upon announcement on Thursday, and will be valid for six months, according to the GAC.
According to the Africa centers for disease control and prevention data on August 9, 13 countries in Africa have reported 17,541 cases of mpox, with 517 deaths.
China has effective capabilities to respond to the potential risks of the spread of mpox, Lu Hongzhou, head of the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, told the Global Times on Friday.
To prevent the spread of mpox, Lu suggested that people should avoid sexual contact with individuals of unknown health status, and stay informed about mpox outbreaks in destination countries and regions when traveling. Lu added that people should avoid coming in contact with animals such as rodents and primates that may carry the virus
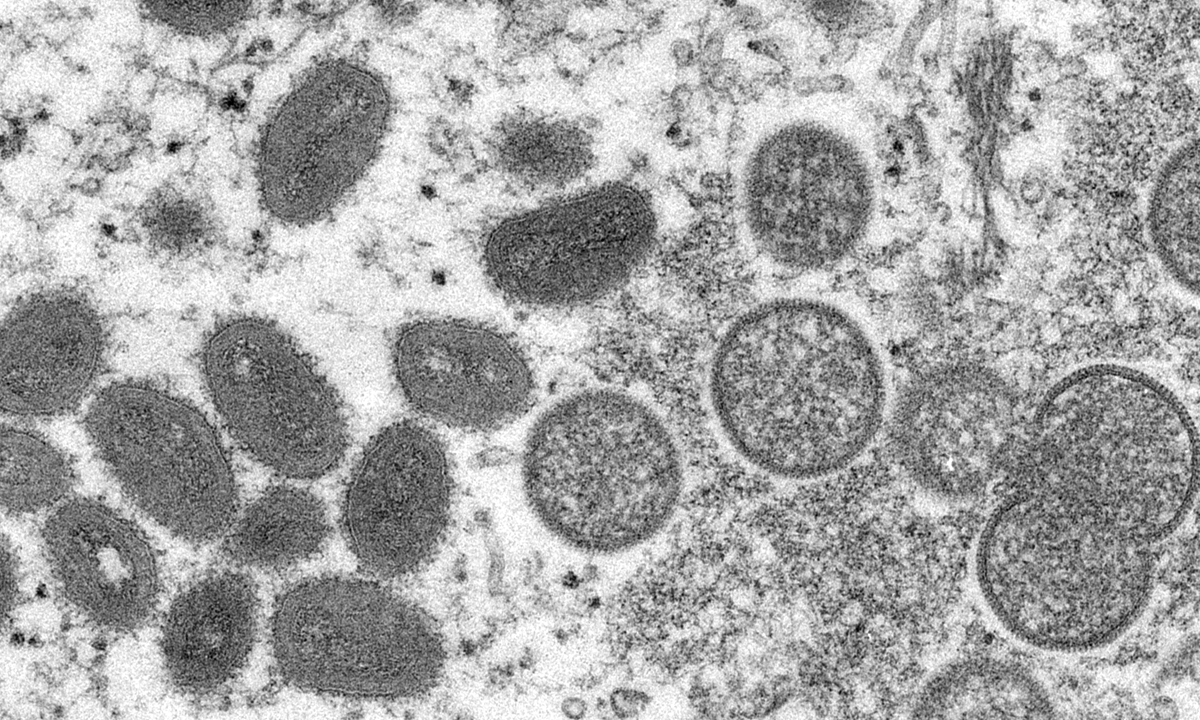
Monkeypox virus particles under a microscope Photo: VCG
Domestic mpox vaccines have not hit the market but research institutions in China have been carrying out clinical trials, Chinese experts said on Monday as the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the mpox surge a public health emergency of international concern - its highest alert level and urged manufacturers to ramp up vaccine production to rein in the spread of a more dangerous strain of the virus.
The WHO urged pharmaceutical firms to ramp up vaccine production on August 16 local time after it warned of the rapid spread of the new Clade 1b variant, a more deadly mpox strain, from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) to other African countries.
Meanwhile, the Stockholm-based European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) on Friday raised its risk level for mpox to "moderate" from "low," a day after global health officials confirmed the first infection caused by a new strain of the virus outside Africa, in Sweden, which was followed by more sporadic cases appearing in the EU, with the overall risk to the population having gone up from "very low" to "low," Reuters reported on Friday.
WHO spokeswoman Margaret Harris urged manufacturers to scale up mpox production, according to a report from Agence France-Presse (AFP) on August 17. The WHO also asked countries with mpox vaccine stockpiles to donate them to countries with ongoing outbreaks, according to the AFP.
According to Lu Hongzhou, head of the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, there is currently no domestic mpox vaccine available in the Chinese mainland, whereas research and preparations are underway, and relevant clinical trials have been promptly carried out.
In July of 2023, the replication-deficient mpox vaccine developed by the China National Pharmaceutical Group Corporation (Sinopharm) and Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention passed the clinical trial application phase with the National Medical Products Administration, making it the earliest domestically developed mpox vaccine to enter the clinical research stage in China.
However, due to the small number of mpox cases across the country and a dispersed population, it is difficult to conduct large-scale clinical studies on the vaccine's efficacy. Additionally, the risks and challenges of such studies are significant, making the development of an mpox vaccine face numerous challenges, Su Jinfeng, a senior biomedical engineer, said in an interview with the Global Times previously.
During the last mpox epidemic on the Chinese mainland, the first imported mpox case was discovered in September 2022 and the first local infection was reported in June 2023. In the following three months between June and August, over 1,000 local confirmed cases were reported across more than 20 provinces across the country, which was triggered by local secondary outbreaks and covert transmission, according to The Beijing News.
On September 20, 2023, mpox was classified as a Category B infectious disease under China's infectious disease control law while China's National Health Commission stated that the mpox epidemic would continue to exist within the country for a certain period of time.
Since the beginning of this year, a total of 357 cases of mpox were reported nationwide as of this June, with no related deaths reported, according to the National Disease Control and Prevention Administration.
Lu said that based on the current prevention and control measures and the domestic epidemic monitoring situation, there is a relatively low possibility of a surge in mpox infections in the Chinese mainland.
China's General Administration of Customs announced on Friday that it would begin screening people and goods entering the country for mpox over the next six months. People arriving from countries where outbreaks have occurred, who have been in contact with mpox cases, or display symptoms should declare this information to customs authorities when entering the country, adding that vehicles, containers, and items from areas with mpox cases should be sanitized.
According to Lu, the mpox virus strain currently circulating on the Chinese mainland belongs to the lineage C.1.1 under the Clade IIb strain, which caused the global outbreak of mpox between 2022 and 2023. Considering peak travel season and the frequent international exchanges, the risk of cross-border transmission of the mpox virus may increase.
However, the mpox virus is primarily transmitted through prolonged close contact, such as sexual activities, skin-to-skin contact, and close-distance breathing or conversations between people, Lu told the Global Times on Monday, noting that its ability to spread between people is relatively weak.
Meanwhile, many people aged 40 and above in the Chinese mainland have already been inoculated with smallpox vaccines, the administration of which, Lu said, has an efficacy of 85 percent in preventing mpox.
Given China's current strict border control and epidemic prevention measures, it is difficult for new cases to spread to the country from overseas. Therefore, the likelihood of a rapid increase in infections in the Chinese mainland like that back in 2023 is relatively low based on the current prevention and control measures and domestic epidemic monitoring, Lu said.
Aside from vaccination, treatments of mpox mainly consist of supportive care and the treatment of complications. Currently, antiviral drugs used in the treatment of mpox include cidofovir, brincidofovir, and tecovirimat. Additionally, ongoing clinical trials of a series of small molecule drugs for mpox have also found that some medicines at lower doses can specifically inhibit the replication of the mpox virus. - By GT staff reporters




No comments:
Post a Comment
rightwaystosuccess@gmail.com